Jeff Phillips, Code Siren, LLC
22 September 2023 - Technology / Code Siren
Introduction
The internet has grown immensely in the past 20 years. In 2003, there were only 600 million internet users worldwide. By 2023, that number had grown to over 5.3 billion
[1], more than half of the global population. This user evolution represents a growth of over 800% in just 20 years.
A study by the University of East Anglia found that the average social media user generates around 100-200 megabytes of digital waste daily. This activity equates to the average internet user generating around 3.65-7.3 gigabytes of digital waste annually.
[2]
The datasphere is a Byzantine system encompassing all types of data, networks, and their dynamic interactions with human groups and norms. The datasphere constantly evolves as new data is generated and existing data is updated, used, or stored.
Main contributors to the bloated datasphere:
⦁ Corporate hoarding and unnecessary data storage: Organizations often store data they no longer need or use. Hoarding can be due to a lack of data governance policies or simply forgetting about the data.
⦁ Multiple data storage locations: Cloud computing-dependent organizations often store the same data in multiple locations, which can lead to redundancy and inefficiency.
⦁ Inefficient data storage technologies: Organizations may be using outdated or inefficient data storage technologies, which can consume more energy and generate more waste. According to IDC, the global datasphere is expected to grow to 291 zettabytes (291 trillion gigabytes) by 2027, more than ten times the data generated in 2016.
[3]
This data explosion is also affected by the rapid acceptance of cloud computing, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT)
[4], and the growing popularity of big data analytics. As more IoT devices and systems are connected to the internet, they generate vast amounts of data.
However, it is important to note that 80% of data is never accessed or used again after storing it. Most enterprises typically only analyze around 10% of the data they collect, and 90% of unstructured data is never analyzed. These statistics challenge the value and necessity of the data that is being collected.
[7]
The Solution to Digital Waste: Ephemeral Technologies
Ephemeral technologies, e.g., temporary chat rooms, offer a promising solution to the growing problem of digital waste. Ephemeral means lasting for a very short time or transitory. These technologies are designed to be temporary and short-lived, reducing the amount of data stored and processed over time.
A key benefit of ephemeral technologies is that they can help reduce digital waste's environmental impact. Data stored on servers and other devices requires energy to power and cool these devices. Ephemeral technologies can help to lessen this impact by decreasing the amount of data that needs to be stored and processed.
Another benefit of ephemeral technologies is that they can help to improve cybersecurity. When data is stored for long periods, it is more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ephemeral technologies can help moderate this risk by deleting data after its use, making it less accessible to attackers.
Ephemeral technology is useful for:
⦁ Confidentiality
⦁ Privacy
⦁ Data Security
⦁ Data minimization (reduce risks)
⦁ Enforce non-retention of data (esp. PII)
⦁ eDiscovery cost reduction
In addition to these benefits, temporary chat rooms and ephemeral messaging can also be used to:
⦁ Promote open and honest communication: Removing the fear of being judged or held accountable for their words, temporary chat rooms, and ephemeral messaging can encourage people to be more open and honest.
⦁ Support collaboration: Temporary chat rooms can facilitate collaboration and teamwork by providing a dedicated space for team members to communicate and share ideas.
⦁ Improve customer service: Ephemeral messaging can provide customers with real-time support without collecting their PII/contact information.
Quantum Rooms™
Quantum Rooms mimic quantum entanglement as two particles are linked, regardless of distance. Measuring one particle's state instantly reveals the other's even billions of miles away. Similarly, Quantum Rooms are workspaces only for individuals with a shared Social Encryption™ (SE) key. Just like the principles of quantum entanglement, the content within Quantum Rooms only exists as long as 1:n individuals view it.
For this reason, Quantum Rooms are both temporal and ephemeral. The moment the last user leaves the Quantum Room, the content is permanently deleted, and the room ceases to exist. Quantum Rooms enable self-destructing content and the creation of private rooms without manually inviting users and managing authorizations.
Quantum Rooms are unique in that they are never created, nor are users ever invited to join the rooms. A QR only exists if 1:n users possess an SE key and happen to have entered the room. Users who have the same SE key(s) will be able to communicate securely with each other via E2EE encryption. Since Quantum Rooms are temporal, individuals can discuss matters of sensitivity and confidentiality without worrying about content management, such as manually setting message expiration rules as required in apps like Signal.
The content in a Quantum Room can be kept-alive, i.e., prevented from auto-deletion, by having at least one person remain in the room. Quantum Room technology allows the users to manually control content expiration by remaining in the room.
Since a given Quantum Room is only visible to individuals with a specific Social Encryption key, deleting an SE key will make entrance into a previously accessible one impossible. They also allow individuals with duplicate SE keys to revisit the same rooms simultaneously without configuring anything within the server. Users who do not have a given SE key will have no way of knowing if any QRs even exist on the server. Quantum Rooms also allow someone to host a server without channels or rooms, i.e., "Empty Server"). The benefit of an empty server is that nobody can create channels or rooms, but only those with SE keys will see which applicable rooms are available to them.
Code Siren, LLC has developed the Quantum Room technology as a feature in
Polynom and is available as an API.
Here are some specific examples of how Quantum Rooms and ephemeral messaging can be used together in collaboration:
⦁ A team of hardware engineers could use Quantum Rooms to collaborate on the design of a new product. They could use ephemeral channels to share sensitive design documents and collaborate without the risk of obsolete versions surviving in the datasphere.
⦁ A team of sales representatives could use Quantum Rooms to collaborate on a sales pitch for a new client. They could use ephemeral channels to share sensitive customer data before the meeting and share notes or transcripts afterward.
⦁ A team of lawyers could use a Quantum Room to collaborate on a legal case. Attorneys can use ephemeral features to share sensitive case documents or privileged data before, during, or after a trial.
Quantum Rooms Flow Diagram
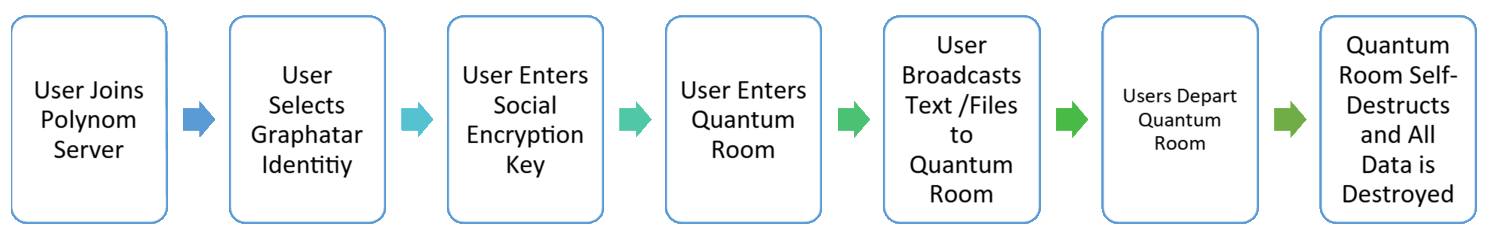
Quantum Room Technology Allows for Data Minimization
The average enterprise user creates between 3-5 gigabytes of files over five years
[5] (and most hard drives have a five-year lifespan). 80% of these documents will never again be accessed after they are saved to storage or a local hard drive
[6]. Much of that information is attached to emails and sent externally. However, sensitive files sent externally using common mechanisms like email or unsecured file-sharing tools like Dropbox will not disappear unless the recipients delete them.
Corporate information hoarding can accelerate costs if the organization becomes involved in legal proceedings – the costs of digital discovery rise in line with data volumes, and keeping so many files for longer than necessary results in unnecessary legal risks (see chart below).
 Source: https://www.perkinscoie.com/images/content/2/4/246721/LIT-OctNov21-EDiscoveryBulletin.pdf
Source: https://www.perkinscoie.com/images/content/2/4/246721/LIT-OctNov21-EDiscoveryBulletin.pdf
Energy Consumption: Global Datasphere
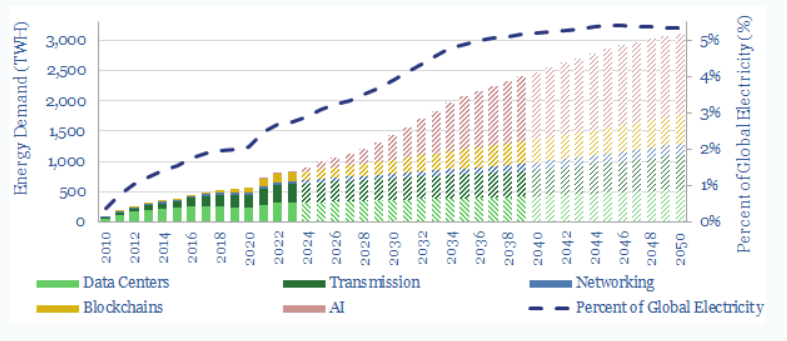 Source: Thunder Said Energy
Source: Thunder Said Energy
Conclusion
In 2022, the global datasphere consumed 800 TWh (trillion watt hours) of electricity. Energy consumption of the Internet will likely double by 2030 due to increased usage of AI and cloud computing, adding 1% to global energy demand and 2.5% to global electricity demand.
[8]
Ephemeral technologies offer a promising solution to the growing problem of digital waste. Quantum Rooms are a unique type of ephemeral technology that can be used for collaboration, communication, and data sharing securely and confidentially.
Ephemeral communications are ushering in a new era of privacy-focused and efficient technology. As the datasphere continues to evolve, Quantum Rooms technology is poised to revolutionize how we interact with messaging and collaboration, transforming our workflow into a more private and efficient tool.




 Read Other Blogs
Read Other Blogs